Classical Mechanics
12/20/2007
Stanford
class with Leonard Susskind.
Goal: create a body of amateur Physicists. people are interested in physics, but not employed by a University. For people who don’t otherwise have access to a graduate course.
Poisson brackets formulation were used to describe phase space and flow in phase space.
Imagine a rotation of a system. Coordinates are ![]() . The rotation transformation may mix the p’s and q’s.
. The rotation transformation may mix the p’s and q’s.
Axiomatic structure of Poisson Brackets
![]() Antisymmetric
Antisymmetric
![]() Linear
Linear
![]() Product rule
Product rule
![]()
![]() (the Kronecker
delta)
(the Kronecker
delta)
![]() and
and ![]()
The momentum is related to the partial derivative.
![]()
Proof:
•
1st show that the relation is true when ![]() is a polynomial.
is a polynomial.
Start with a constant term. Any constant will do.
![]() by product rule
by product rule
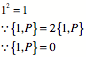
Now try 1st power of ![]() .
.
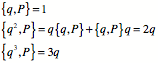
The pattern is that of a derivative. The proof is by mathematical induction.
and similarly
![]()
The time derivative along a trajectory
as before,
![]()
Example:
![]()
then
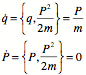
Canonical Transformations of Poisson Brackets
Question: what are the allowable transformations that preserve the Poisson Bracket properties?
Example of a transformation.
![]() does not
preserve properties since
does not
preserve properties since ![]() ?
?
However
![]() does
preserve the properties.
does
preserve the properties.
Example: Rotation.
We need to check only ![]() since
since ![]() by antisymmetry!
by antisymmetry!
![]()
![]()
Therefore the structure is preserved.
Canonical transformations keep the relations unchanged.
Investigate an infinitesimal transformation. (suppress indices)
![]()
Drop infinitesimal quadratic terms.
![]()
It is necessary and sufficient that the following be true in order to maintain the Poisson Bracket structure:
![]()
Assume a generator function ![]() . Now substitute into a canonical transformation.
. Now substitute into a canonical transformation.
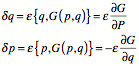
Always defines a canonical transformation.
![]()
So ![]() is also a
generator of another flow, another canonical transformation.
is also a
generator of another flow, another canonical transformation.
![]()
to get
![]()
therefore since
![]()
then
![]()
Consider canonical transformations that do not change the energy. That transformation is a symmetry.
Consider the time derivative of ![]()
![]()
Don’t know where this goes:
![]()
If the energy is not changed, then
![]() Generator
commutes with the Hamiltonian so that
Generator
commutes with the Hamiltonian so that ![]() is conserved.
is conserved.
![]()
Example: A canonical transformation (a rotation). Let
![]()
Let
![]()
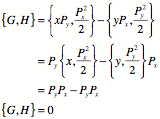
Therefore ![]() is conserved
under the rotation.
is conserved
under the rotation.
Make up a new system. Let
![]()
then
![]()
Therefore, circular motion.
Example:
![]()
then
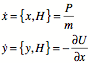
Homework: Prepare for Quantum Mechanics next semester. Look at iTunes “Quantum Entanglement, the Logic of Discrete Systems”.
The end of the semester.